Are you constantly battling fatigue, struggling to lose weight, or feeling like your body just isn’t working as efficiently as it used to? You might be experiencing slow metabolism symptoms.
While many factors contribute to weight gain, a slow metabolism can make it significantly harder to shed pounds and maintain a healthy weight.
Your metabolism is not fixed—it can be influenced by factors like diet, sleep, and exercise. Small changes can lead to significant improvements over time.”
Dr. Eric Berg
This comprehensive guide will help you identify potential signs of a slow metabolism, understand what impacts your metabolic rate, and explore practical strategies for preventing slow metabolism symptoms and revving it up naturally.
You can get your body working with you, not against you.
What Is Metabolism and How Does It Work?
Metabolism describes all the chemical processes your body performs to keep you alive and functioning, even at rest.
It encompasses the conversion of food and drink into energy. This energy fuels essential activities like breathing, blood circulation, cell growth and repair, and even thinking.
Metabolism also involves managing your hormone levels and regulating your body temperature. The rate at which your body uses energy is known as your metabolic rate1.
Basal Metabolic Rate
Basal metabolic rate, often called BMR, represents the minimum number of calories your body needs just to carry out those essential life-sustaining functions while at rest. Imagine your body at complete rest, not even digesting.
This value accounts for about 50%-80% of your total daily energy use, according to researchers at Mayo Clinic.
Resting Metabolic Rate
Similar to BMR, resting metabolic rate (RMR) reflects your calorie burn at rest. However, it also considers calories used for activities like digestion.
Though often used interchangeably with BMR, it represents a slightly higher energy expenditure.
Factors that Impact Metabolic Rate
Several things determine your individual metabolic rate2, including age.
This explains why some people seem to eat whatever they want and still stay slim, while others struggle to maintain a healthy weight. Factors including genetics and sex also play a role.
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Age | Metabolic rate naturally declines with age, mainly due to decreased muscle mass. As you age, your slower metabolism can contribute to weight gain. |
| Sex | Men typically have faster metabolic rates than women due to a greater proportion of lean muscle mass. |
| Body Size & Composition | Larger individuals with more muscle mass have higher metabolic rates as their bodies need more energy for upkeep. They have a faster metabolism due to their body composition. |
| Genetics | Genes play a role in how effectively your body uses energy, influencing individual differences in metabolic rate. |
| Hormonal Factors | Thyroid hormone levels significantly affect metabolic rate, and fluctuations can cause both increases and decreases. Other hormonal changes related to aging, stress, or specific conditions like PCOS also influence calorie burn. Hormone imbalance can be a major factor in how your metabolism functions. |
Signs of Slow Metabolism Symptoms
Many slow metabolism symptoms can mimic other conditions, so it’s always important to consult your doctor or a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis. Here are common clues to be aware of:
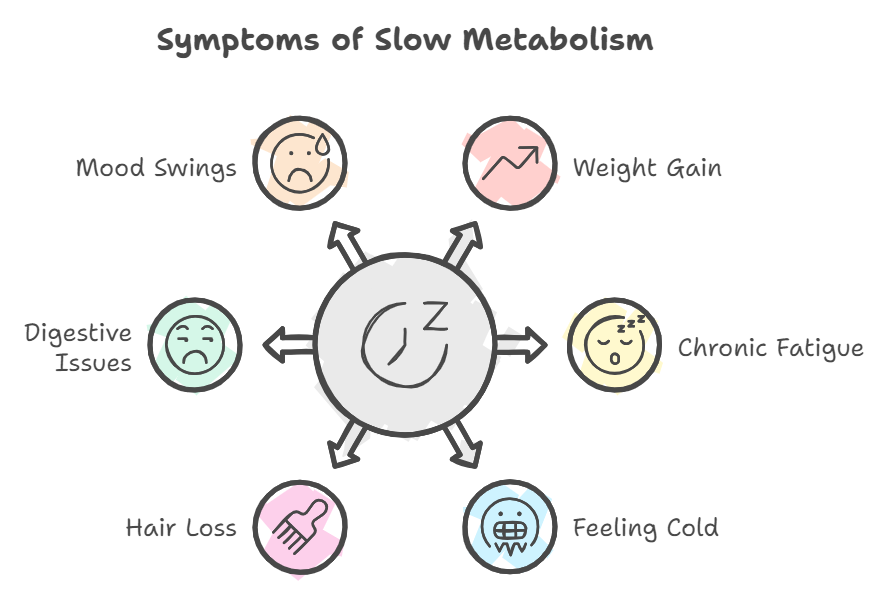
Weight Gain or Difficulty Losing It
One of the most frustrating slow metabolism symptoms is unexplained weight gain or an inability to shed those extra pounds, even when trying to eat right and exercise regularly.
Because a sluggish metabolism reduces the rate at which your body burns calories, even healthy efforts may not produce the desired results.
This can be incredibly frustrating when trying to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Chronic Fatigue and Low Energy
Feeling tired all the time, even after a good night’s sleep, is another hallmark of slow metabolism symptoms.
If basic activities leave you feeling drained, this could be a signal your metabolism needs a boost. You might have low daily energy levels.
Feeling Cold Often
Metabolic processes generate heat, so a less efficient metabolism can leave you feeling cold easily, even in warm environments.
Your body might struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature because your inner furnace isn’t operating at full capacity.
Hair Loss or Dry Skin
Healthy metabolic function plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, which directly impacts hair and skin health.
Hormonal imbalances associated with slow metabolism symptoms, like low thyroid levels, often manifest as dry skin or brittle, thinning hair loss3. You might even have trouble shaving.
Digestive Issues and Cravings
It may sound surprising, but slow metabolism symptoms can even involve digestive sluggishness and cravings for sugary or processed foods.
As your body struggles to process what you eat efficiently, you may experience constipation, bloating, and cravings that are tough to ignore. It’s a vicious cycle that further hinders weight management.
Mood Swings and Difficulty Concentrating
When your body isn’t running smoothly, your mind often suffers too. Mood swings, brain fog, and difficulty concentrating can also be linked to slow metabolism symptoms.
It’s no surprise since these intricate bodily systems are interconnected and influence each other. Your physical activity can also be impacted.
Debunking Common Myths About Metabolism
Many myths about metabolism can cause confusion and bad habits. Let’s clear up some of the most common misconceptions:
Myth 1: Eating Small, Frequent Meals Boosts Metabolism
Many believe that eating small meals every few hours will “stoke the metabolic fire.” It will keep it burning all day. However, research shows that meal frequency has little impact on your metabolism.
Meal frequency is less important than total calorie intake and nutrient quality for weight management and metabolism. Eat three larger meals or five smaller ones. What matters is your total caloric balance.
Myth 2: Metabolism Doesn’t Change With Age
It’s a common belief that metabolism remains the same throughout life, but that’s not true. As we age, muscle mass decreases, leading to a slower resting metabolic rate.
This is why many people experience weight gain or find it harder to lose weight as they grow older. But, strength training and regular exercise can help. They can maintain muscle mass and keep your metabolism active.
How to lose weight with a slow metabolism? Um mit einem langsamen Stoffwechsel Gewicht zu verlieren, sind regelmäßige Bewegung, insbesondere Krafttraining, und eine proteinreiche Ernährung entscheidend, da sie den Kalorienverbrauch erhöhen.
Auch ausreichend Schlaf und Stressmanagement unterstützen den Stoffwechsel und fördern die Gewichtsabnahme.
Myth 3: Skipping Meals Slows Down Your Metabolism
Can fasting slow metabolism? Fasting or skipping meals can lower your metabolic rate. But, it doesn’t “ruin” your metabolism, as some believe.
Short-term fasting can lower energy use. But, your body adapts when you resume normal eating. But, skipping meals may lead to overeating later.
This could cause weight gain. So, occasional fasting won’t destroy your metabolism. But, it’s vital to eat balanced meals in the long term.
Myth 4: You Can’t Change Your Metabolism
Some people think they’re doomed by genetics to have a slow metabolism and there’s nothing they can do about it.
Genetics matter, but lifestyle factors matter more. Exercise, diet, and sleep can greatly affect your metabolic rate.
Resistance training, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can boost your metabolism. This is true, regardless of your genes.
Myth 5: Exercise Has No Long-Term Effect On Metabolism
It’s true that exercise raises your metabolism for a bit. Many think this effect is short-lived and offers no long-term benefits.
However, building muscle increases your basal metabolic rate (BMR)4 because muscle burns more calories than fat, even at rest.
Over time, regular strength training and high-intensity exercise can have a lasting impact on how many calories you burn each day.
Myth 6: “Fat-Burning Foods” Will Significantly Speed Up Your Metabolism
Certain foods, like green tea, spicy peppers, or grapefruit, are often marketed as “fat-burning” foods. While some of these foods may slightly increase your metabolic rate, the effect is usually minimal.
No single food is going to drastically boost your metabolism or prevent slow metabolism symptoms.
Sustainable metabolic improvement comes from a combination of healthy eating habits, exercise, and lifestyle choices, not from relying on so-called “miracle” foods.
Practical Tips on How to Slow Metabolism
The good news is, there are things you can do to give your metabolism the support it needs. Implementing some of these strategies could help boost your energy levels, manage your weight, and improve overall well-being.
Prioritize Protein Intake
Protein helps you feel fuller longer, increases the amount of calories your body burns during digestion (also called the thermic effect of food), and supports building lean muscle mass, which burns more calories than fat.
Excellent protein sources include fish, eggs, beans, poultry, and low-fat dairy.
To prevent your metabolic rate from dropping, aim for 0.5 grams of protein per pound of your body weight5 per day, or at least 1.2 grams per kg. Eating healthy food and getting enough protein are good indicators of a healthy lifestyle.
How to slow down metabolism? A high-protein diet can prevent slow metabolism symptoms. This is important when trying to lose or maintain weight. If you’re looking for ways to easily boost your protein intake, check out our comprehensive guide for helpful tips.
Don’t Cut Calories Drastically
While limiting calorie intake for weight loss makes sense, severely restricting your diet can actually backfire.
Your body adapts to survival mode when deprived, decreasing its metabolic rate and holding onto calories as a safety mechanism.
Multiple studies confirm that a calorie intake of fewer than 1,000 per day can significantly impact your metabolic rate.
Gradual weight loss approaches tend to be more sustainable and allow your metabolism to keep humming. You also don’t want to throw your hormones off balance.
Stay Hydrated
Don’t underestimate the power of drinking enough water throughout the day.
Proper hydration is essential for many metabolic processes and can aid in calorie burning. Sip water regularly and listen to your body’s signals of thirst.
Make Time For Movement
Consistent strength training can increase lean muscle mass, which in turn elevates your metabolic rate. Explore weightlifting, yoga, Pilates, and bodyweight exercises to keep things challenging and engaging.
If you are asking, how to slow down your metabolism: Aim for 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise five days per week. This will increase your basal metabolic rate and help you burn more calories.
Boost NEAT
NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis) describes energy burned through daily activities not related to planned exercise. Increasing NEAT can significantly impact your metabolic rate and improve your body’s efficiency in using energy.
Simply incorporating more movement into your day, like standing more often, taking the stairs, or walking to run errands, can make a difference. Someone with a slower metabolic rate might find themselves sitting for long periods.
Get Consistent Quality Sleep
Chronic sleep deprivation not only contributes to weight gain and disrupts hunger hormones, it also affects your metabolism directly by slowing the rate at which you burn calories. Strive for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep each night to support a healthy metabolic rate.
Studies reveal that skimping on sleep can cause metabolic dysregulation, leaving your body less efficient in using energy. When your body doesn’t perform basic functions properly, like getting enough sleep, you will feel the effects.
Choose Smart Snacks
While late-night eating is linked to weight gain for several reasons, including less time to burn off those calories before bed, opting for nutrient-rich snacks can help support stable energy levels throughout the day and prevent crashes.
This in turn promotes a healthy metabolic rate.
Reduce Added Sugar
High intake of added sugar, particularly fructose, is strongly linked to increased weight gain.
These sugars mess with your body’s ability to effectively burn calories. You might think the metabolic impacts of high-fructose corn syrup and whole wheat are similar, but this isn’t the case.
Excess consumption is a recipe for metabolic disaster. If you are someone with excess kilos, you will want to monitor your sugar intake.
Frequently Asked Questions
What slows metabolism?
Several factors can slow down metabolism, including age, hormonal imbalances, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. As you age, muscle mass tends to decrease, which can lead to a slower metabolic rate. Additionally, stress, inadequate sleep, and certain medical conditions like hypothyroidism can also contribute to a slower metabolism.
Does metabolism slow with age?
Ja, der Stoffwechsel verlangsamt sich mit zunehmendem Alter, da Muskelmasse abnimmt und der Energiebedarf sinkt. Regelmäßige Bewegung und eine ausgewogene Ernährung können jedoch helfen, den Stoffwechsel aktiv zu halten und altersbedingten Veränderungen entgegenzuwirken.
How do I slow down my metabolism?
To boost your metabolism, focus on regular physical activity, especially strength training, which increases lean muscle mass. Eating a balanced diet with sufficient protein, staying hydrated, and ensuring quality sleep are also crucial. Avoid drastic calorie cutting, as this can cause your body to slow down its metabolic processes.
Conclusion
Understanding your metabolism is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While it’s tempting to look for quick fixes or fall into common myths, the reality is that slow metabolism symptoms are influenced by a combination of factors, including genetics, age, muscle mass, and daily habits.
By focusing on sustainable changes—like incorporating regular physical activity, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, and managing stress—you can positively impact your metabolic rate over time.
Remember, it’s not just about eating less or exercising more—it’s about creating a balanced lifestyle that works with your body, not against it. Focus on gradual, sustainable changes, and you’ll be on your way to a healthier, more energized you.
Small Step, Big Impact
If you suspect a slow metabolism, start by tracking your symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider, and making small lifestyle changes like increasing physical activity and eating more protein-rich foods.
Listen to this article
This is an AI generated Podcast version of the article.
- https://www.webmd.com/fitness-exercise/difference-between-bmr-and-rmr[↩]
- https://blog.nasm.org/nutrition/resting-metabolic-rate-how-to-calculate-and-improve-yours#~=Resting%20metabolic%20rate%20is%20the,1%25%20increase%20in%20body%20fatness.[↩]
- https://guthealth.org/can-an-unhealthy-gut-cause-hair-loss[↩]
- https://www.verywellfit.com/what-is-bmr-or-basal-metabolic-rate-3495380[↩]
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5639963[↩]



