You’ve probably heard about retinoids, those powerhouse ingredients in skin care. Maybe you’re already using retinol or even prescription tretinoin. But have you heard about its close relative, retinaldehyde? This ingredient is getting a lot of attention, and for good reason, often appearing in advanced retinaldehyde cream serum formulations.
“Retinaldehyde offers a compelling balance between efficacy and tolerability, making it an excellent choice for individuals seeking the benefits of retinoids without the associated irritation.”
Dr. Davin Lim
Understanding this specific form of Vitamin A can help you make smarter choices for your skin care routine. We’ll break down what retinaldehyde does, how it stacks up against other retinoids, and how you can add it to your regimen safely. Getting familiar with retinaldehyde could be a significant step in achieving your skin goals, leading to smoother skin and enhanced skin radiance.
What Exactly is Retinaldehyde?
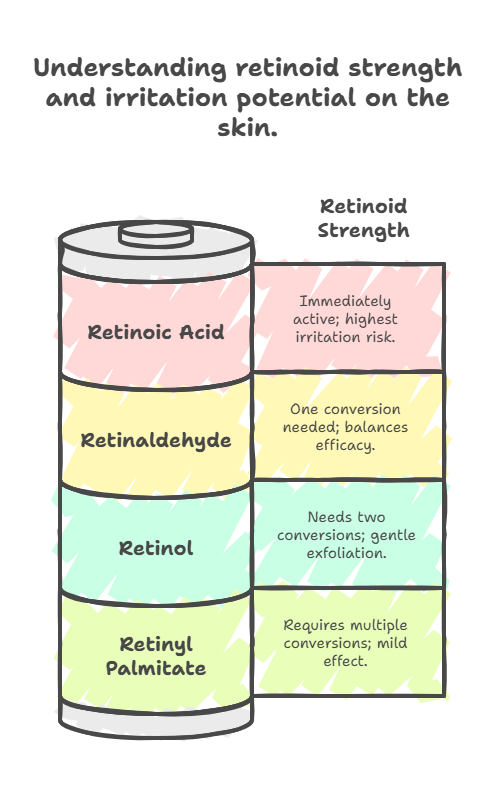
Retinaldehyde, sometimes called just ‘retinal’, is part of the retinoid family. This group includes all Vitamin A derivatives used in skin care. Think of it like a spectrum: retinyl palmitate is among the gentlest, then comes retinol, then retinaldehyde, and finally, the strongest is retinoic acid (like tretinoin, often a prescription-strength retinoid).
So, retinaldehyde sits effectively in the middle of the potency range. It’s recognized for being stronger and faster-acting than the widely used retinol. However, it’s generally considered gentler than prescription retinoic acid, which is beneficial for many skin types, including those prone to sensitivity1.
It’s also a naturally occurring form of Vitamin A in our bodies. It participates in the pathway where Vitamin A eventually becomes the active form within the skin. This biological connection partly explains its rising popularity in cosmetic products and cosmetic dermatology circles.
How Does Retinaldehyde Work on the Skin?
Let’s discuss the science simply. For any retinoid to deliver benefits like improving texture, reducing lines, or fighting acne, it must be converted into retinoic acid. This is the active form your skin cells recognize and utilize.
The conversion path is crucial. Retinol requires two steps to become retinoic acid: first converting to retinaldehyde, then to retinoic acid. Retinaldehyde, conversely, only needs one step: retinaldehyde converted directly into retinoic acid.
This single conversion step is highly significant. It allows retinaldehyde to function faster and potentially more effectively than retinol. Some research indicates it could be considerably quicker, making it an attractive choice for those wanting prompt results from their skin care regimen2.
Major Benefits of Using Retinaldehyde
Why the growing interest in retinaldehyde? It provides many of the same excellent benefits as other retinoids but often strikes a better balance between antiaging efficacy and gentleness. Let’s examine the key advantages.
Boosts Collagen Production
Similar to its retinoid relatives, retinaldehyde excels at signaling skin cells to produce more collagen—the essential protein responsible for keeping skin firm and youthful. As skin aging progresses, natural collagen production decreases, contributing to wrinkles and sagging. To explore how retinoids can improve your skin’s appearance, check out our guide on retinol cream.
By stimulating new collagen synthesis, retinoldehyde aids in smoothing fine lines and wrinkles. It helps improve skin elasticity over time. This contributes to a more resilient and younger-looking complexion.
Speeds Up Skin Cell Turnover
Our skin naturally sheds dead cells and replaces them with new ones in a process called cell turnover. This cycle slows down with age. A slower turnover can result in dull-looking and rough-feeling skin.
Retinoldehyde acts like an accelerator for cell turnover. It facilitates the quicker shedding of old, dead skin cells. This process reveals fresher, brighter skin beneath and assists in keeping pores clear, contributing to overall skin radiance3.
Improves Skin Texture and Tone
With increased cell turnover and collagen production, retinoldehyde can markedly refine skin texture. It helps the skin feel smoother and appear more even. It can also assist in diminishing hyperpigmentation, such as sun spots or post-acne marks4.
Consistent use may lead to a more uniform skin tone. The improvement in brightness is often noticeable. This makes retinaldehyde a valuable ingredient for addressing issues like unevenness and lack of luminosity, leading to smoother skin.
Fights Acne
Retinoids were initially developed for acne treatment, and retinoldehyde continues this function. It helps prevent pore blockages by accelerating cell turnover. Fewer clogs reduce the likelihood of blackheads, whiteheads, and pimples, making it suitable even for oily skin types.
Retinaldehyde also possesses direct antibacterial properties, especially against Cutibacterium acnes, the bacteria associated with acne. This dual action – clearing pores and combating bacteria – makes it effective for managing breakouts. Some find it more tolerable than alternatives like benzoyl peroxide or even prescription options.
Retinaldehyde vs. Other Retinoids: Key Differences
Selecting the appropriate retinoid can seem complex. How does retinoldehyde genuinely measure up against retinol or prescription tretinoin? The primary distinctions involve conversion steps, potency, and the potential for skin irritation.
Retinaldehyde vs. Retinol
This comparison is frequent among skin care users. Both are available over-the-counter in various forms, from serums to creams. Recall the conversion pathway discussion?
Retinol undergoes two steps to become active retinoic acid, whereas retinaldehyde requires only one. This inherently makes retinoldehyde faster-acting and potentially a more potent form than retinol, even when concentrations seem similar. A retinaldehyde cream might therefore show results faster than a standard retinol product.
Due to its increased potency, retinaldehyde might initially cause more irritation than retinol, although it remains generally better tolerated than prescription retinoic acid. Many current retinoldehyde cream serum products incorporate soothing agents like certain seed oil extracts to mitigate this. Finding a well-formulated product, perhaps one recommended by an advisory board of dermatologists, is beneficial.
Retinaldehyde vs. Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin)
Retinoic acid, such as the common prescription tretinoin, represents the ‘active’ form. It requires no conversion upon application to the skin. This positions it as the most powerful retinoid accessible.
While exceptionally effective, retinoic acid also presents the highest risk of side effects, collectively known as retinization. Common issues include redness, peeling, dryness, and heightened sensitivity. Managing these often requires careful supervision from a board-certified dermatologist5.
Retinaldehyde offers a compelling middle ground. It delivers significant results—likely more apparent than retinol for many individuals—without the pronounced irritation potential of prescription retinoic acid. This makes it a strong over-the-counter alternative, especially if your skin reacts poorly to tretinoin or if you desire something more impactful than standard retinol. Some randomized controlled studies have explored the antiaging efficacy of retinaldehyde-based cream compared to placebo or other ingredients.
Other exfoliating acids like glycolic acid, lactic acid, salicylic acid (found in BHA liquid products), and azelaic acid work differently. While retinoids regulate cell turnover from deeper layers, these acids primarily exfoliate the surface. Combining them requires caution; for instance, using a glycolic acid peel or azelaic acid salicylic acid treatments on the same night as retinaldehyde could increase skin irritation, especially initially. Sometimes, alternating nights or using milder combinations is suggested.
Here’s a simple table summarizing the key points:
| Feature | Retinyl Palmitate | Retinol | Retinaldehyde | Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Steps to Active Form | Multiple Steps | Two (Retinol → Retinaldehyde → Retinoic Acid) | One (Retinaldehyde → Retinoic Acid) | Zero (Already active) |
| Speed of Action | Slowest | Slower | Faster | Fastest |
| Potency | Lowest | Lower | Moderate-High | Highest |
| Irritation Potential | Lowest | Lower | Moderate | Highest |
| Availability | Over-the-counter | Over-the-counter | Over-the-counter | Prescription required |
Are There Potential Side Effects?
Yes, similar to all retinoids, retinaldehyde can induce side effects, particularly during the initial usage phase. This adjustment period is commonly referred to as ‘retinization’. It occurs as your skin acclimates to the accelerated cell turnover.
Typical side effects may include:
- Dry skin.
- Peeling or flaking.
- Redness.
- Mild stinging or itching.
- Increased sun sensitivity.
These effects are generally temporary and tend to diminish as your skin adapts over several weeks. However, careful introduction of retinaldehyde is vital to minimize discomfort and skin irritation. Addressing skin hydration needs during this time is important.
Daily application of sunscreen SPF 30 or higher is absolutely crucial when using any retinoid, retinaldehyde included. Retinoids increase the skin’s susceptibility to sun damage and sunburn. Protecting your skin diligently helps prevent adverse effects and protects against long-term issues like premature skin aging and even skin cancer risk.
How to Incorporate Retinaldehyde into Your Skincare Routine
Interested in trying retinaldehyde? A smart, gradual introduction helps maximize benefits while minimizing irritation. Follow these guidelines for a successful start.
Start Slowly
Avoid applying it nightly right away. Start by using a pea-sized amount just 2-3 times per week. Allow your skin several weeks to adjust before you increase frequency.
Pay close attention to your skin’s response. If substantial redness or peeling occurs, reduce the frequency. Patience is essential; significant results require time, but consistent, tolerated use is the goal.
Apply to Dry Skin
Applying retinaldehyde to damp skin can sometimes enhance absorption, potentially increasing irritation. It is generally recommended to wait about 10-20 minutes after cleansing. Ensure your skin is completely dry before applying your retinaldehyde product, whether it’s a cream serum or a standalone cream.
Use the ‘Sandwich’ Method if Needed
For those with sensitive skin or concerns about irritation, the sandwich method can be helpful. Apply a thin layer of a simple, non-comedogenic moisturizer first. Then, apply the retinaldehyde, followed by another layer of moisturizer.
This technique creates a buffer that can lessen potential dryness and sensitivity, making the potent form more tolerable. It doesn’t usually reduce effectiveness significantly but makes the experience gentler, particularly for dry skin types. Good skin hydration is key.
Choose the Right Strength
Retinaldehyde cosmetic products are available in various concentrations, typically from 0.01% up to 0.1% or occasionally higher. If you are new to retinoids or possess sensitive skin, begin with a lower concentration. You can gradually transition to a stronger product once your skin demonstrates tolerance.
A higher strength does not automatically guarantee faster or superior results. Consistent application of a strength your skin handles well provides more long-term benefits. Overdoing it early on can cause irritation that forces discontinuation.
Combine with Supportive Ingredients
Seek retinaldehyde products formulated with hydrating and calming ingredients. Components like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, niacinamide, panthenol, and certain types of seed oil can help counteract dryness. These ingredients support your skin barrier while the retinaldehyde performs its functions.
Avoid using other potentially irritating active ingredients during the same application routine as retinaldehyde, at least initially. This includes strong chemical exfoliants like high-concentration glycolic acid, salicylic acid (acid salicylic), or even some forms of azelaic acid salicylic acid blends. Using multiple potent actives simultaneously, such as undergoing glycolic acid peel sessions while starting retinaldehyde, increases the risk of skin irritation. Let your skin adapt first.
Consider using gentler acids like lactic acid on alternate nights once your skin adjusts. Also, be cautious with Vitamin C serums in the same routine initially. Separate potent actives between morning and evening routines or use them on different days.
Always Use Sunscreen
This point bears repeating: daily sunscreen is indispensable. Retinaldehyde increases photosensitivity, meaning greater sun sensitivity. Protect your skin every morning using a broad-spectrum sunscreen SPF 30 or higher, regardless of weather conditions.
Who Should Consider Using Retinaldehyde?
Retinaldehyde can be an excellent choice for many individuals. It might be especially suitable if you:
- Have used retinol but desire potentially quicker or more evident results without needing a prescription-strength retinoid.
- Possess sensitive skin that found prescription retinoids overly irritating, yet still want effective anti-aging or acne management benefits. This could apply to managing dry skin or oily skin types.
- Are addressing both signs of skin aging (lines, wrinkles, firmness loss) and occasional breakouts.
- Are searching for an over-the-counter retinoid with robust evidence for improving skin texture and tone. Perhaps after seeing positive results in a randomized controlled trial or systematic review.
- Want a product effective around the delicate eye area; look for a specifically formulated retinaldehyde eye cream.
However, not everyone requires the most potent form available. If you are content with your current retinol product results, switching might not be necessary. But if you are curious about advancing your retinoid usage, retinaldehyde is certainly worth exploring.
Individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid all retinoids, including retinaldehyde. Always consult with your doctor or a board-certified dermatologist if you have specific skin conditions (like eczema or rosacea), concerns about skin cancer history, or before introducing potent new active ingredients. As one expert, Dr. [Insert Name if known, otherwise remove “explains dr”], might state, personalized advice is often best.
Finding Quality Retinaldehyde Products
As retinaldehyde’s popularity grows, more retinaldehyde cream and serum options appear. How do you select a high-quality one? Prioritize reputable brands recognized for stable and effective formulations.
Retinaldehyde can be less stable than retinol, potentially degrading if not formulated and packaged properly. Look for opaque, airless pump dispensers, which help protect the ingredient from light and air exposure. Examine ingredient lists for the concentration and the presence of supportive elements like peptides, antioxidants, or hydrating agents like seed oil.
Don’t let price be the sole determining factor. Focus on brands that invest in research and employ proven stabilization technologies for their retinaldehyde. Reading reviews can be helpful; look for comments marked ‘review helpful’ from users with similar skin concerns or types (e.g., dry skin, oily skin). Some brands might offer incentives like free shipping or include samples with gift cards.
Keep an eye on social media or brand websites for information, but verify claims with independent research or dermatologist recommendations where possible. Be aware of marketing claims and focus on formulation quality. Tracking technologies used by some brands might offer insights into product batches or authenticity, but this is less common.
Patience and Consistency are Your Allies
Effective skin care is rarely about immediate transformations. Whether you opt for retinol, retinaldehyde, or another active ingredient, consistent, long-term use yields lasting results. Typically, it takes several weeks, often 8-12, or even months, to observe significant improvements in fine lines, skin texture, hyperpigmentation, or acne control.
Adhere to your routine, introduce retinaldehyde gradually, safeguard your skin with sunscreen SPF daily, and maintain good skin hydration. Trust the journey. Achieving healthy, radiant skin is a marathon, not a sprint, and retinaldehyde can be a potent ally along the way.
Consider taking baseline and progress photos in consistent lighting conditions. Changes can be subtle initially, and visual documentation helps track improvements in skin radiance and achieving smoother skin. Seeing progress can be highly motivating to continue your efforts.
Conclusion
Retinaldehyde stands out as an impressive retinoid, effectively bridging the gap between over-the-counter retinol and prescription retinoic acid. Its single-step conversion pathway allows it to work faster than retinol, offering significant benefits for addressing skin aging concerns and managing acne. While initial skin irritation is possible, introducing a retinaldehyde cream or serum carefully and maintaining consistent use can lead to smoother, firmer, and clearer skin for many people.
If you are looking for potent results from your skin care with potentially better tolerability than prescription options, exploring retinaldehyde-based cosmetic products could be a highly beneficial step for your skin’s health and appearance. Remember the importance of sun protection and consulting a professional if you have underlying skin conditions or concerns. Incorporating this powerful Vitamin A derivative might just elevate your entire routine.
Small Step, Big Impact
Integrating retinaldehyde into your nightly skincare routine can enhance collagen production and accelerate cell turnover, leading to firmer, more radiant skin. Begin with a low concentration, apply it every other night, and always use sunscreen during the day to protect your rejuvenated skin.
Listen to this article
This is an AI generated Podcast version of the article.
- https://int.medik8.com/pages/retinaldehyde-skincare-what-is-it-how-to-use-it-benefits?srsltid=AfmBOooiS-pXr5CkYK_KnDND45MvSa1ZpWzs0bW7Rl1pzUU4cXfQr0wM[↩]
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699641/[↩]
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6791161/[↩]
- https://drdavinlim.com/a-z-skin-care/retinaldehyde/[↩]
- https://www.medik8.com/pages/acids-retinoids-how-to-use-them-in-your-skincare?srsltid=AfmBOooEC7eXyHo7ULo-7ahGgDLGv5Y-FCDGqwMWtc_IG_ROrVM1Nvat[↩]



